Please use the following information to answer the following question(s) .
You work for a company selling tropical rain forest plants commonly found in the understory of the forest. These plants are shade tolerant and can be grown indoors because they require low light. Your employer wants you to find out what is the best type of light to maximize growth of these understory plants. Using a full spectrum of natural light would cause these plants to die because they are a shade-tolerant plant species.
From your biology class, you recall that the light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis involve pigment molecules that absorb light of specific wavelengths. You also remember the experiments done by the German biologist Theodor Engelmann, in which he separated light using a prism into different wavelengths and then determined which wavelengths were best for promoting photosynthesis in the algae species he was examining. Your goal is to determine which wavelengths (colors) of light are best for promoting photosynthesis to enhance growth in your species of plant. To achieve this, you grew your plants under different wavelengths of light and measured their growth rates. The wavelengths were measured in nanometers (nm) , and the growth rate was measured in millimeters per day (mm/day) . The data you collected are as follows:
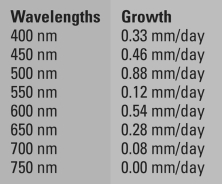
Make a bar graph plotting growth rates on the y-axis and wavelengths of light on the x-axis. Referring to your graph, answer the following question(s) :
-Why do some plant species require shaded conditions while other plant species require bright sunlight?
Definitions:
Additional Paid-In Capital
The amount paid by investors above the par value of a stock during equity issuance, reflecting excess funds contributed by shareholders.
Rights Exercised
Entails the act of utilizing legal or contractual entitlements by individuals or entities.
Par Stock
The nominal or face value assigned to shares of stock by the corporation's charter, which may differ from their market value.
Q3: The first step of the Calvin cycle
Q4: An individual with (naturally)curly hair and an
Q4: Which one of the following will prevent
Q16: The idea that life regularly arises from
Q19: Under what conditions is Cramér's V used
Q21: What global climatic change gave gymnosperms an
Q31: Like plants,fungi have _; however,in plants they
Q42: Examine the drawing of an atom below.The
Q42: The region of DNA where RNA synthesis
Q45: What is the greatest threat to birds