Free Trade Game
Free trade occurs when goods and services between countries flow unhindered by government-imposed restrictions such as tariffs, quotas, and antidumping laws that are often designed to protect domestic industries. Although it is well known that free trade creates winners and losers, a broad consensus exists among most economists that free trade has a large and unambiguous net gain for society as a whole. For example, Robert Whaples (2006) finds in a survey of economists that "87.5% agree that the U.S. should eliminate remaining tariffs and other barriers to trade" and that "90.1% disagree with the suggestion that the U.S. should restrict employers from outsourcing work to foreign countries." Despite this consensus, it is not at all clear that countries will actually adopt policies promoting free trade.
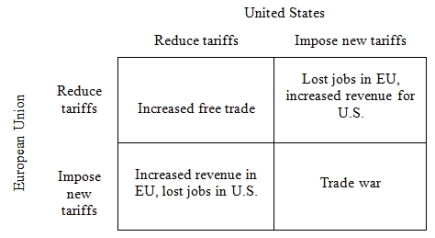
Consider the following strategic situation in which the United States and the European Union (EU) are engaged in trade negotiations. Both countries must decide whether to reduce their tariffs or impose new tariffs. The best outcome for both countries is for them to impose new tariffs and for the other side to reduce tariffs; they could then export more easily to the other country and they would obtain increased revenue from the new tariffs. The worst outcome for both countries is for them to reduce tariffs and for the other country to increase tariffs; they would lose jobs as a result of reduced exports and the other country would benefit from their lower tariffs. Of the remaining two outcomes, both countries prefer the outcome in which they reduce tariffs to the one in which they both impose new tariffs. If both countries reduce their tariffs, then each country can benefit from increased free trade. If both countries impose new tariffs, there is a trade war in which each country sees a decline in trade and a loss of jobs. Based on this story, the preference ordering for the EU over the four possible outcomes is:
• Impose; Reduce > ; Reduce > Impose; Impose > Reduce; Impose.
And the preference ordering for the United States is:
• Reduce; Impose > Reduce; Reduce > Impose; Impose > Impose; Reduce,
where the EU's action is given first, the United States' action is given second, and ">" means "is strictly preferred to."
Using the ordinal preferences (4, 3, 2, 1) to capture these preference orderings, fill in the empty payoff matrix. Based on the preference orderings in the Free Trade Game.
Figure 1: Free Trade Game
-What is (are) the expected outcome (outcomes) of the game?
Definitions:
Field Name
The label or identifier assigned to a specific field in a database or form, which describes the kind of data it holds.
Column
A vertical division of a page or text, or a structural element in databases used to store a particular type of information.
Design View
A database view that allows users to create and modify database structures in applications like Microsoft Access.
Create Tab
an action in computer applications to open a new tab, allowing users to multitask or organize work in separate views.
Q1: The Value Management Strategy Map identifies all
Q3: The economic growth rate in Bangladesh in
Q4: The last step of the 6D MVMS
Q6: All of the following are stages in
Q7: Your city has declared a state of
Q8: Members of a market segment are _.<br>A)
Q8: Is the sign that Fish found on
Q11: A "reliable" measure is one that<br>A) corresponds
Q24: What is the subgame perfect Nash equilibrium
Q26: Consider the results from Model 1 in