Scenario: The table below shows the reservation values of ten buyers and a seller for a loaf of bread. Each buyer would buy at most one loaf and the seller can make up to ten loaves. Initially trades happen under the market mechanism with each agent making a decision according to the market price and his or her own reservation value. Then the government imposes a price ceiling of $1.00 per unit.
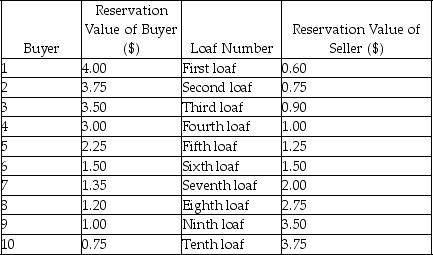
-Refer to the scenario above.Suppose that,after the price ceiling is imposed,the shortage forces buyers to offer bribes to the seller in order to secure a loaf.If each buyer offered as much as his or her reservation value,and the seller sells to the highest bidders,how many loaves will exchange hands? Is the outcome efficient?
Definitions:
Double-declining-balance Method
An accelerated depreciation method that doubles the depreciation expense compared to the straight-line method.
Depreciation Expense
Systematically dividing the expense of a tangible asset over the period it remains useful.
Scrap Value
The estimated worth of an asset's materials when the asset is deemed no longer useful and is intended to be disposed of or recycled.
Straight-line Method
A method of calculating depreciation by evenly spreading the cost of an asset over its expected useful life.
Q14: Refer to the figure above.What is the
Q59: A steel-producing factory in North Palladia generates
Q63: Takashi,an Asian,and Sally,a Caucasian,apply for a job
Q90: The quantity effect of a price decrease
Q91: Refer to the figure above.The line S₁
Q119: An increase in the income tax rate
Q159: The tax incidence on sellers is higher
Q192: Which of the following statements is true
Q212: Refer to the above scenario.If a price
Q265: The following figure shows the demand curve