Scenario: This problem applies the principle of optimization covered in Chapter 5 to the problem of choosing how many hours to work. Paul has to decide how many hours to work per day. His boss is willing to give Paul whatever hours Paul wants up to 8 hours. All else being equal, he would rather not work, that is, Paul has positive marginal benefit from each hour of leisure. But he is an avid collector of presidential campaign buttons. The more leisure he takes, the fewer buttons he can afford. So Paul faces a trade-off between leisure and buttons. Each button costs $1.00. The table below shows Paul's marginal benefits from leisure (MBlₑᵢsᵤᵣₑ) and buttons (MBbᵤttₒn) .
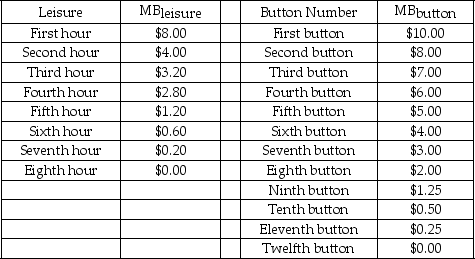
-Refer to the scenario above.If the hourly wage is $1.00,what is the maximum possible number of buttons Paul can afford?
Definitions:
Immune System
The body's defense mechanism against pathogens, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites.
Insulin Resistance
A condition in which the body's cells do not respond properly to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Type 1 Diabetes
A chronic condition where the pancreas produces little or no insulin, requiring individuals to manage their blood sugar levels through insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes
A chronic condition affecting the way the body processes blood sugar (glucose), characterized by insulin resistance.
Q5: A price ceiling refers to _.<br>A) the
Q11: Refer to Goldin and Rouse's study of
Q31: Refer to the table above.If Beth earns
Q45: An efficient price is a price set
Q105: Each citizen in Nexus City has to
Q121: Refer to the scenario above.If the first
Q150: Refer to the above scenario.Your marginal tax
Q210: The congestion charge is an example of
Q214: Suppose that a firm in a competitive
Q227: Compared to a perfectly competitive industry,_ in