Scenario: This problem applies the principle of optimization covered in Chapter 5 to the problem of choosing how many hours to work. Paul has to decide how many hours to work per day. His boss is willing to give Paul whatever hours Paul wants up to 8 hours. All else being equal, he would rather not work, that is, Paul has positive marginal benefit from each hour of leisure. But he is an avid collector of presidential campaign buttons. The more leisure he takes, the fewer buttons he can afford. So Paul faces a trade-off between leisure and buttons. Each button costs $1.00. The table below shows Paul's marginal benefits from leisure (MBlₑᵢsᵤᵣₑ) and buttons (MBbᵤttₒn) .
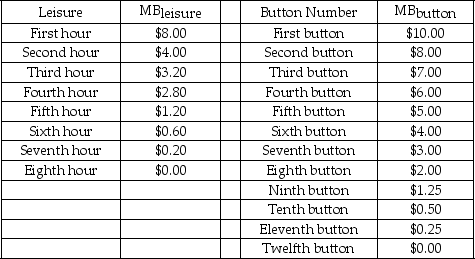
-Refer to the scenario above.If the hourly wage is $1.00,how many hours would Paul choose to work? How many buttons would he buy?
Definitions:
Social Deviations
Noncriminal departures from norms that are nonetheless subject to official control. Some members of the public regard them as somewhat harmful, whereas other members of the public do not.
Tougher Penalties
Increased severity of punishments or consequences for criminal activities aimed at deterring crime.
Crime Rates
The number of crimes committed per unit of population within a specified time period.
Prison
A facility in which people are forcibly held and denied a range of personal freedoms under the authority of the state as punishment for crimes.
Q6: Which of the following is not an
Q25: The figure below shows the cost and
Q47: Which of the following goods is rival
Q61: Refer to the scenario above.From Cass's point
Q77: Which of the following is an example
Q82: Refer to the scenario above.To restore the
Q149: What are the types of market power?
Q175: In 1973,economist Steven N.S.Cheung wrote an article
Q180: Refer to the scenario above.Which of the
Q202: A _ tax is similar to a