Scenario: This problem applies the principle of optimization covered in Chapter 5 to the problem of choosing how many hours to work. Paul has to decide how many hours to work per day. His boss is willing to give Paul whatever hours Paul wants up to 8 hours. All else being equal, he would rather not work, that is, Paul has positive marginal benefit from each hour of leisure. But he is an avid collector of presidential campaign buttons. The more leisure he takes, the fewer buttons he can afford. So Paul faces a trade-off between leisure and buttons. Each button costs $1.00. The table below shows Paul's marginal benefits from leisure (MBlₑᵢsᵤᵣₑ) and buttons (MBbᵤttₒn) .
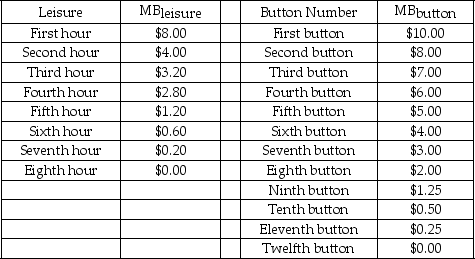
-Refer to the scenario above.If the hourly wage is $1.00,what is the maximum possible number of buttons Paul can afford?
Definitions:
Customer Waiting Time
Customer waiting time is the duration a customer has to wait before receiving a service or product, influencing satisfaction and perception of service quality.
WIP Inventory
Work-in-Process (WIP) Inventory consists of materials and components that have begun their transformation process but are not yet completed products.
Longest Processing Time
A rule used in scheduling that prioritizes jobs or tasks according to those with the longest duration first.
Lateness
The state of being late or delayed in comparison to a predetermined schedule or deadline.
Q5: A price ceiling refers to _.<br>A) the
Q38: Refer to the figure above.If the market
Q61: Other things remaining the same,which of the
Q160: Which of the following activities is most
Q163: A game is called a simultaneous-move game
Q169: The firm's value of marginal product of
Q176: Which of the following is likely to
Q188: Which of the following market structures provides
Q203: You are good at creating Web sites.You
Q209: Most municipalities and states in the northeastern