Scenario: This problem applies the principle of optimization covered in Chapter 5 to the problem of choosing how many hours to work. Paul has to decide how many hours to work per day. His boss is willing to give Paul whatever hours Paul wants up to 8 hours. All else being equal, he would rather not work, that is, Paul has positive marginal benefit from each hour of leisure. But he is an avid collector of presidential campaign buttons. The more leisure he takes, the fewer buttons he can afford. So Paul faces a trade-off between leisure and buttons. Each button costs $1.00. The table below shows Paul's marginal benefits from leisure (MBlₑᵢsᵤᵣₑ) and buttons (MBbᵤttₒn) .
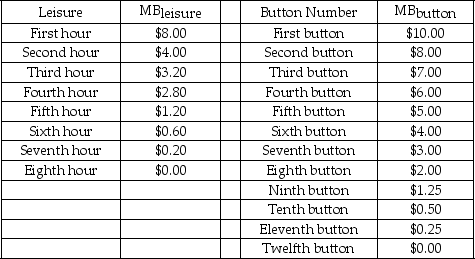
-Refer to the scenario above.If the hourly wage is $1.60,how many hours would Paul choose to work? How many buttons would he buy?
Definitions:
Tech Support
Assistance provided by companies to consumers facing technical problems or issues with electronic devices or software.
Time-Driven
Refers to activities or systems where performance or output is measured in relation to the amount of time taken to complete them.
Activity-Based Costing
Accounting practice that assigns costs to products or services based on the precise resources they consume, offering more accuracy in costing.
Receiving Calls
The action or process of answering or accepting incoming telephone calls.
Q3: A college graduate getting paid more than
Q49: Refer to the figure above.What is the
Q56: Refer to the scenario above.Which of the
Q62: Refer to the figure above.If the rental
Q101: Refer to the scenario above.When Tobac Co.'s
Q129: A profit-maximizing monopolist produces the quantity at
Q135: Which of the following is an implication
Q155: Advances in computing power are an example
Q210: Which of the following is true of
Q215: Refer to the figure above.What kind of