Table 16-3
The information in the table below shows the total demand for premium-channel digital cable TV subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each digital cable TV operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide premium digital channels in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the premium channel service to a household is zero.
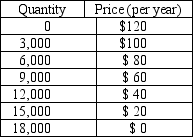
-Refer to Table 16-3.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing digital cable TV companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to collude on the price and quantity of premium digital channel subscriptions to sell.How much profit will each firm earn when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium?
Definitions:
Self-Driving Car
A vehicle equipped with technology that allows it to navigate and operate without human intervention, using sensors and artificial intelligence to control driving functions.
Advertisement
A public promotion of some product or service, aimed at attracting interest, engagement, and sales.
Product Advertisements
Promotional messages and strategies aimed at informing or persuading customers about products.
Individual Brand
A marketing strategy where each product is marketed under its own unique brand name, emphasizing its distinct qualities and targeting a specific consumer segment.
Q21: When a profit-maximizing firm in a competitive
Q25: Refer to Scenario 15-3.What is the deadweight
Q62: The production decisions of perfectly competitive firms
Q73: Economists assume that monopolists behave as<br>A)cost minimizers.<br>B)profit
Q93: Critics of markets that are characterized by
Q104: In the prisoners' dilemma game,self-interest leads<br>A)each prisoner
Q127: When new firms enter a perfectly competitive
Q135: The practice of requiring someone to buy
Q174: In the short run,a firm in a
Q194: In the long run,<br>A)monopolistically competitive firms earn