Figure 51.6 Use the following information and the figure below when answering the corresponding question(s) .
The following are an abstract and figure from a paper that explores the evolutionary relationship between a protein kinase and behavior (M. Fitzpatrick and M. Sokolowski. 2004. In search of food: Exploring the evolutionary link between cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) and behaviour. Integrative and Comparative Biology 44:28-36) .
Abstract:
Despite an immense amount of variation in organisms throughout the animal kingdom many of their genes show substantial conservation in DNA sequence and protein function. Here we explore the potential for a conserved evolutionary relationship between genes and their behavioural phenotypes. We investigate the evolutionary history of cGMP-dependent protein kinase (PKG) and its possible conserved function in food-related behaviours. First identified for its role in the foraging behaviour of fruit flies, the PKG encoded by the foraging gene had since been associated with the maturation of behaviour (from nurse to forager) in honey bees and the roaming and dwelling food-related locomotion in nematodes. These parallels encouraged us to construct protein phylogenies using 32 PKG sequences that include 19 species. Our analyses suggest five possible evolutionary histories that can explain the apparent conserved link between PKG and behaviour in fruit flies, honey bees and nematodes. Three of these raise the hypothesis that PKG influences the food-related behaviours of a wide variety of animals including vertebrates. Moreover it appears that the PKG gene was duplicated some time between the evolution of nematodes and a common ancestor of vertebrates and insects whereby current evidence suggest only the for-like PKG might be associated with food-related behaviour.
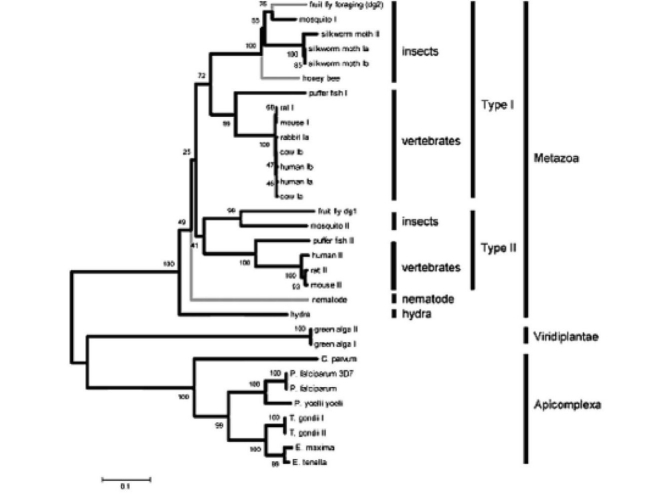
Neighbour joining trees depicting the evolutionary relationships of 32 PKG kinase domain and C-terminal amino acid sequences spanning 19 species of protozoans and metazoans. Values at the nodes represent the results of 5000 bootstrap replications. Lineages with known behavioral links with PKG are indicated by grey branches.
-Using the information above,and knowing that the PKG encoded by the foraging gene has recently been associated with the maturation of out-of-nest behavior in honeybees,what would be a logical explanation for this relationship?
Definitions:
Elderly
Refers to individuals, typically of age 65 and over, who are in the later stage of their life cycle.
Loneliest Age Group
Refers to specific age demographics shown by research to experience the highest levels of loneliness, often subject to change based on societal and individual factors.
Attributional Style
A psychological concept referring to how individuals explain the causes of events and behaviors, particularly in the context of success or failure.
Interdependence
A relationship in which two or more entities rely on each other for resources, support, or benefits, creating a mutual dependency.
Q1: Which nervous pathway does sensory information travel
Q2: All of the following are examples of
Q4: In the figure above,which of the arrows
Q14: Home blood typing kits reveal an individual's
Q15: Food and its products of degradation move
Q19: Which are the only two interaction types
Q22: When primary producers expend energy to build
Q25: Which of the following statements about Iraq's
Q29: Marine biologists recently warned that the stock
Q35: Based on the figure above,and given the