Table 2-16
-Refer to Table 2-12.This table shows the number of labor hours required to produce a digital camera and a bushel of wheat in China and South Korea.
a.Assume each country has a total of 9,000 labor hours to devote to the production of the two goods and draw the production possibilities frontier for each country.Put "Digital Camera" on the horizontal axis and "Wheat" on the vertical axis.Be sure to identify the intercept values on your graphs.
b.Suppose each country allocates 60% of its labor hours to wheat production and 40% to the production of digital cameras.Complete Table 2-13 below to show each country's output of the two products.
Table 2-13: Production and Consumption with no Trade
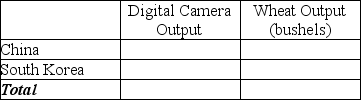
c.If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce, identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers.Label China's consumption point "C" and South Korea's consumption point "K."
d.Suppose the two countries specialize and trade.Which country should produce digital cameras and which should produce wheat? Explain your answer.
e.Complete Table 2-14 below to show each country's output with specialization.
Table 2-14: Output with Specialization
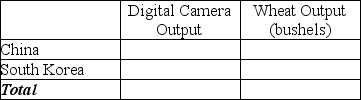
f.Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so, by how much?
g.Suppose China and South Korea agree to trade so that in exchange for 1,200 bushels of wheat, the exporter of wheat receives 48 digital cameras.Complete Table 2-15 below to show each country's consumption bundle after trade.
Table 2-15: Consumption with Trade

h.Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier.Label these points "B" for China and "J" for South Korea.
i.Has trade made the two countries better off? Explain your answer.
Definitions:
Percentage Calculation
The process of finding a part of a whole number or quantity, typically expressed as a fraction of 100.
Tax Rate
The percentage at which an individual or corporation is taxed.
Income Tax
A tax levied by a government directly on individuals' or organizations' income.
Percentage Calculation
Percentage calculation involves determining the part of a whole in terms of 100, used in various financial and statistical contexts to express proportions.
Q5: Refer to Figure 3-2.A decrease in the
Q15: The town of Harmonia gives away all
Q30: Scarcity refers to a situation in which
Q43: Refer to Table 4-3.The table above lists
Q84: Refer to Table 2-11.Scotland has a comparative
Q97: Refer to Figure 3-3.The figure above shows
Q105: Even if the population declines, scarcity will
Q123: a.Draw a production possibilities frontier for a
Q148: Assume that potatoes are an inferior good.Which
Q232: In a report made to the U.S.Congress