Figure 13-17 -Refer to Figure 13-17.What Is the Allocatively Efficient Output for Allocatively
Figure 13-17
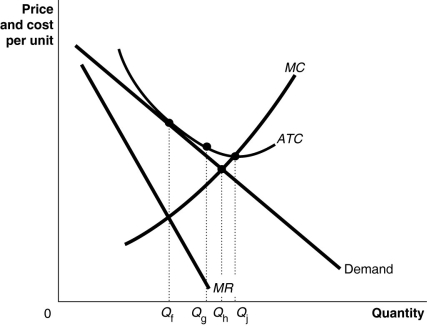
-Refer to Figure 13-17.What is the allocatively efficient output for the firm represented in the diagram?
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers.
Excise Tax
A tax levied on specific goods, services, or transactions, often specific types of products such as gasoline, cigarettes, or alcohol.
Equilibrium Price
The cost at which the amount of a good consumers want to buy matches the amount producers are willing to sell, achieving a state of equilibrium in the market.
Allocative Efficiency
A state of the economy in which production is in line with consumer preferences; every good or service is produced up to the point where the last unit provides a benefit to consumers equal to the cost of producing it.
Q15: For a firm in a perfectly competitive
Q33: If the marginal product of labor is
Q105: Refer to Figure 13-4.What is the area
Q113: There are several types of barriers to
Q141: Refer to Table 14-3.Is there a dominant
Q158: A firm that is first to the
Q165: If the market price is $25 in
Q203: Refer to Figure 14-2.Now suppose that the
Q217: When firms exit a perfectly competitive industry,
Q284: The perfectly competitive market structure benefits consumers