Figure 15-8
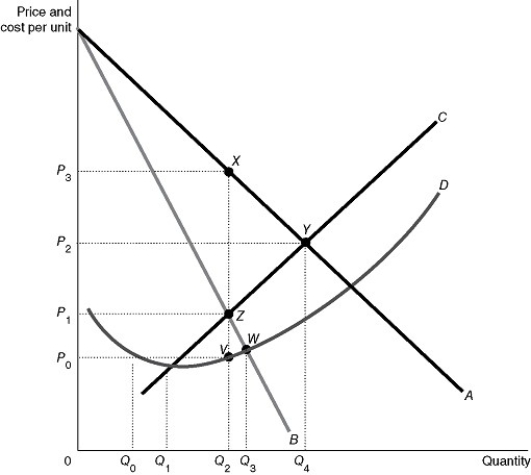
Figure 15-8 reflects the cost and revenue structure for a monopoly that has been in business for a very long time.
-Refer to Figure 15-8.Use the figure above to answer the following questions.
a. Identify the curves labeled A and B.Identify the curve which contains both point Y and point Z.Identify the curve which contains both point V and point W.
b.What is the profit-maximizing quantity and what price will the monopolist charge?
c.What area represents total revenue at the profit-maximizing output level?
d.What area represents total cost at the profit-maximizing output level?
e.What area represents profit?
f.What is the profit per unit (average profit)at the profit-maximizing output level?
g.If this industry was organized as a perfectly competitive industry, what would be the profit-maximizing price and quantity?
h.What area represents the deadweight loss as a result of a monopoly?
Definitions:
DNA Replication
The biological process of producing two identical replicas of DNA from one original DNA molecule, essential for cell division.
Complementary Base Pairing
The pairing of bases by hydrogen bond formation in double-stranded nucleic acids according to the base pairing rules: adenine pairs with thymine (in DNA) or uracil (in RNA), and guanine pairs with cytosine.
Purines
A group of heterocyclic aromatic organic compounds, including adenine and guanine, that are key components of DNA and RNA.
Pyrimidines
A type of organic compound, characterized by a single six-membered ring, that includes cytosine, thymine, and uracil, essential components of nucleic acids.
Q7: The four-firm concentration ratio in the breakfast
Q28: The only firms that do not have
Q50: Refer to Table 16-2.What is the total
Q93: Refer to Table 14-1.Is there a dominant
Q117: When an oligopoly is in a Nash
Q128: Which of the following statements about the
Q137: Economists played a key role in the
Q138: How do the price and quantity of
Q214: Charging different prices to different consumers for
Q241: In an oligopoly, firms can increase their