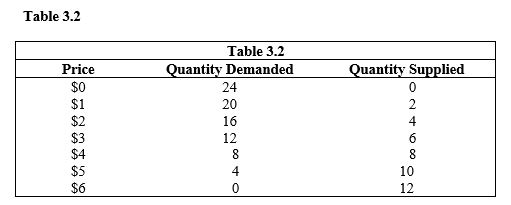
-In Table 3.2, the equilibrium quantity is
Definitions:
Covariation Principle
A concept in social psychology indicating that behavior is attributed to potential causes that co-occur consistently with the observed effect.
Covariation Principle
A principle used to explain how people attribute cause; they note the pattern between the presence or absence of possible causal factors and whether the behavior occurs.
Inference
The process of drawing conclusions from available evidence or premises, often used in reasoning and problem-solving.
Kelley's Covariation Model
A psychological theory that explains how individuals attribute cause to events based on the pattern of covariation between event and possible causes, considering consistency, distinctiveness, and consensus.
Q13: If a firm has total revenue of
Q29: Diamonds are more expensive than water because
Q37: If the price of a product decreases,
Q47: From a point of equilibrium, which of
Q64: Average revenue is<br>A) the price at which
Q67: Most economists like perfect competition because<br>A) it
Q69: Elimination of sugar quotas have _ the
Q77: Which of the following is least likely
Q93: Wage differentials exist because not all workers
Q135: In Figure 2.3, the initial demand curve