Table 17-2
The information in the table depicts the total demand for wireless Internet subscriptions in a small urban market. Assume that each wireless Internet operator pays a fixed cost of $100,000 (per year) to provide wireless Internet in the market area and that the marginal cost of providing the wireless Internet service to a household is zero.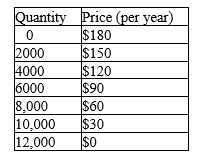
-Refer to Table 17-2.Assume that there are two profit-maximizing wireless Internet companies operating in this market.Further assume that they are not able to "collude" on price and quantity of wireless Internet subscriptions to sell.What price will wireless Internet subscriptions be sold at when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium
Definitions:
Partial Equilibrium
Partial equilibrium is an analysis of the equilibrium position of a single market or sector within the wider economy, without considering interactions with other markets or sectors.
Substitutes
Two goods for which an increase in the price of one leads to an increase in the quantity demanded of the other.
General Equilibrium Analysis
Simultaneous determination of the prices and quantities in all relevant markets, taking feedback effects into account.
Partial Equilibrium Analysis
Determination of equilibrium prices and quantities in a market independent of effects from other markets.
Q30: Which statement do economists generally agree on<br>A)The
Q36: Refer to Table 17-3.If both firms follow
Q50: Which scenario best represents a monopoly situation<br>A)Bill
Q69: Refer to Scenario 16-1.As a result of
Q74: For the oligopolist that does not collude
Q117: Which two curves are tangent to one
Q155: What is the defining characteristic of a
Q164: Refer to Scenario 15-1.If dozens of residents
Q166: Refer to Scenario 19-3.In a competitive market
Q230: When a firm experiences zero-profit equilibrium,the firm's