Use the table below to answer the following questions.
Table 24.5.1
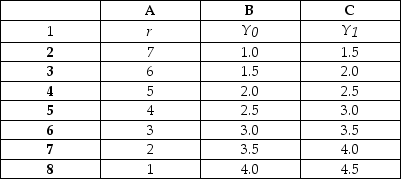
-Refer to Table 24.5.1. The spreadsheet provides information about the demand for money in Minland. Column A is the nominal interest rate, r. Columns B and C show the quantity of money demanded at two different levels of real GDP: Y₀ is $10 billion and Y₁ is $20 billion.
The quantity of money is $3 billion. Real GDP is $20 billion.
If the interest rate is greater than 4 percent a year,
Definitions:
Depreciation Expense
The allocation of the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life, reflecting the asset's consumption, wear and tear, or obsolescence.
Estimated Useful Life
The expected period over which a company anticipates deriving benefits from an asset before it becomes obsolete or too costly to maintain.
Units-Of-Production Depreciation
A depreciation method that allocates the cost of an asset over its useful life based on its output or usage rather than the passage of time.
Straight-Line Depreciation
A method of allocating the cost of a tangible asset over its useful life in equal annual increments.
Q1: Refer to Figure 26.3.4. The changes represented<br>A)cannot
Q1: An assumption of the new growth theory
Q4: The Canadian government increases its expenditure on
Q15: If real GDP is $12,150 billion and
Q20: Investment is financed by which of the
Q50: Potential GDP is<br>A)the maximum amount of GDP
Q64: Everything else remaining the same, an increase
Q71: Refer to Table 20.4.4. The table provides
Q88: Refer to Figure 26.3.1. As Econoworld automatically
Q115: If aggregate planned expenditure exceeds real GDP,