The new owner of a beauty shop is trying to decide whether to hire one, two, or three beauticians. She estimates that profits next year (in thousands of dollars) will vary with demand for her services, and she has estimated demand in three categories, low, medium, and high.
If she feels the chances of low, medium, and high demand are 50 percent, 20 percent, and 30 percent respectively, what are the expected annual profits for the number of beauticians she will decide to hire? 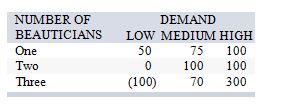
Definitions:
Cognitive Processing
The mental activities involved in the acquisition, storage, manipulation, and retrieval of information, encompassing processes such as perception, memory, and reasoning.
Savant Syndrome
A condition where a person with significant mental disabilities demonstrates certain abilities far in excess of average.
Abstract Concepts
Ideas that do not have a physical, tangible reality and are often complex, such as justice, love, or freedom.
Factor Analysis
A statistical method used to describe variability among observed, correlated variables in terms of a potentially lower number of unobserved variables called factors.
Q1: Which of the following makes using present
Q3: Option A has an expected value of
Q19: When determining the timing and degree of
Q20: A location analysis has been narrowed
Q26: The fundamental purpose for the existence of
Q39: A manufacturing cell allows the production of
Q45: One disadvantage of specialization is worker dissatisfaction.
Q71: Consider the following decision scenario: <img src="https://d2lvgg3v3hfg70.cloudfront.net/TB2632/.jpg"
Q78: Reducing consumer choices makes service more efficient.
Q96: A methods and measurements analyst for