Figure 11-18
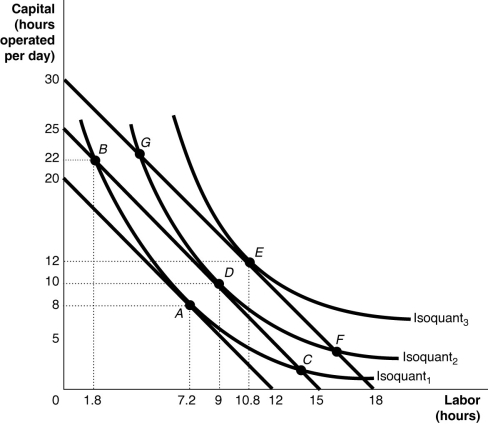
-Refer to Figure 11-18.Starting from point E, a movement along the isocost to point F
Definitions:
Receivables
Money owed to a company by its customers or other parties for goods or services that have been delivered but not yet paid for.
Older Accounts
Refers to accounts receivable that have been outstanding for a longer period, often categorized by how long they have been unpaid (e.g., 30 days, 60 days).
Aging of Receivables Method
This is an accounting technique used to estimate uncollectible receivables by analyzing and classifying accounts receivable according to their age.
Accounts Receivable Turnover
A financial ratio that measures how many times a company can turn its accounts receivable into cash during a period.
Q3: A monopolistically competitive firm chooses<br>A)both the quantity
Q8: The law of diminishing marginal returns<br>A)explains why
Q70: The demand curve for an inferior good
Q75: Refer to Figure 10-1.Which of the following
Q133: Which of the following does not explain
Q189: Alan Krueger conducted a survey of fans
Q281: As output increases, the distance between average
Q284: Once a product becomes established, network externalities
Q297: What happens to the absolute value of
Q318: Refer to Figure 11-7.When output level is