Morphologically, Species A is very similar to four other species, B-E. Yet the nucleotide sequence deep within an intron in a gene shared by all five of these eukaryotic species is quite different in Species A compared to that of the other four species when one studies the nucleotides present at each position.
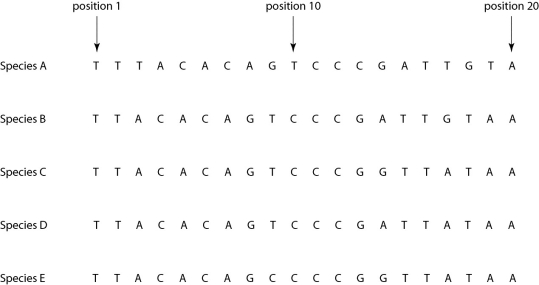 Figure 26.4
Figure 26.4
-If the sequence of Species A differs from that of the other four species due to simple misalignment, then what should the computer software find when it compares the sequence of Species A to those of the other four species?
Definitions:
Hypothetical Claim
A statement or assertion based on assumptions or possibilities, not necessarily on facts or reality.
Deductive Argument
A type of logical argument in which the conclusion necessarily follows from the premises if they are true.
Valid
In logic, a term describing an argument where, if the premises are true, the conclusion must also be true.
Argument Form
The structure or pattern of reasoning used in constructing a logical argument.
Q6: What is proteomics?<br>A)the linkage of each gene
Q6: Which of the following techniques used to
Q13: Ultimately, which of these serves as the
Q14: In order to identify a specific restriction
Q48: The common ancestors of birds and mammals
Q58: Based on the tabular data, and assuming
Q58: Bryophytes never formed forests (mats, yes, but
Q63: Which statement about variation is True?<br>A)All phenotypic
Q68: Select the factor most likely to have
Q78: Nitrogenase, the enzyme that catalyzes nitrogen fixation,