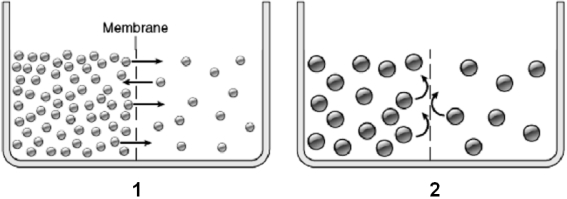
Use the figure above to answer the corresponding questions.Assume the membrane is always permeable to water.
-In beaker 1, the solution on the right side of the membrane
a.could eventually have the same concentration of green solute particles as the solution on the left side of the membrane
b.could eventually have the same osmolarity as the solution on the left side of the membrane
c.currently has a lower osmotic pressure than the solution on the left side of the membrane
d.is currently losing water
e.all of these
Definitions:
Deep Basin
A large depression on the earth's surface, often below sea level, characterized by significant depths and possibly housing sedimentary formations or resources.
Mid-ocean Ridge
A mid-ocean ridge is an underwater mountain system formed by plate tectonics, characterized by a rift at the crest through which magma rises, creating new oceanic crust.
Back-arc Spreading
A geologic process occurring behind a subduction zone, where new oceanic crust is formed by the spreading and melting of the mantle.
Plate-tectonic Setting
The geological and geographical context of an area in relation to the movement and interaction of tectonic plates.
Q28: When EPSPs occurring simultaneously from two different
Q43: Electrical gradient for K⁺ at EK⁺
Q108: During the resting potential<br>A)K+ ions leave the
Q124: The hydrophobic interior of the lipid bilayer
Q138: A transport maximum is associated with carriers
Q143: Myelinated axons conduct impulses much faster because<br>A)the
Q149: Competes with glycine for receptors
Q189: _ are organelles that may possibly transport
Q197: Cocaine blocks the binding of dopamine at
Q253: An electroencephalogram is a record of action