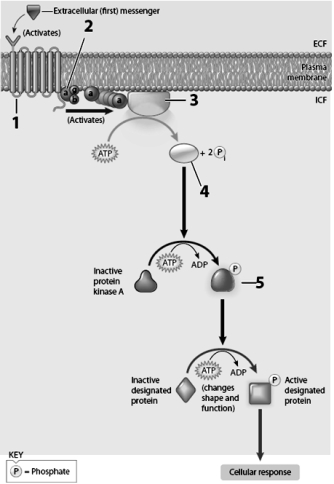
Use this figure to answer the corresponding questions.
-Describe an action potential and explain why a region of the membrane that is in the absolute refractory period cannot experience another action potential until repolarization is complete.Include the following in your answer: voltage-gated Na⁺ channels, voltage-gated K⁺ channels, activation gate, inactivation gate, threshold voltage, increasing membrane potential, and decreasing membrane potential.
Definitions:
Tympanic Percussion
A method used in physical examinations to produce sounds by tapping on the body's surface, particularly over the tympanic area to assess air presence in body cavities.
Palpable Spleen
A spleen that is detectable upon physical examination, often indicating enlargement due to various health conditions.
Gastric Acid Secretion
The process of producing stomach acid, which aids in digestion and protects against pathogens in the gastrointestinal tract.
Esophageal Emptying
The process by which the esophagus clears food and liquids from the throat to the stomach, essential for normal digestion.
Q16: Cystic fibrosis is caused by abnormal<br>A)accumulation of
Q29: Neuropeptides<br>A)are sometimes co-secreted along with classical neurotransmitters<br>B)are
Q51: The concentration of substance X outside the
Q87: The time following an action potential during
Q168: The sense of body position is<br>A)somatosensory<br>B)integrated in
Q186: A region on the medial surface of
Q198: The nodes of Ranvier are<br>A)action potential recordings<br>B)breaks
Q218: When chemically-gated Na⁺ channels open, the membrane<br>A)hyperpolarizes<br>B)repolarizes<br>C)depolarizes<br>D)becomes
Q233: In the retina, photoreceptor cells do not
Q242: Which pairing has the most closely related