For the hydrolysis of ATP to ADP + 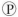 ᵢ, the free energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) . In the cellular environment, however, the free energy change is about -13 kcal/mol. What can we conclude about the free energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and
ᵢ, the free energy change is -7.3 kcal/mol under standard conditions (1 M concentration of both reactants and products) . In the cellular environment, however, the free energy change is about -13 kcal/mol. What can we conclude about the free energy change for the formation of ATP from ADP and 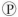 ᵢ under cellular conditions?
ᵢ under cellular conditions?
Definitions:
Foreign Particles
Tiny, extraneous substances not naturally part of a system, often causing harm or disruption.
Active Site
Pocket in an enzyme where substrates react and are converted to products.
Substrate
Molecule that an enzyme acts upon and converts to a product; reactant in an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Chemical reactions involving the transfer of electrons between two substances, altering their oxidation states and often producing energy.
Q2: In the small airways of the lung,
Q6: A number of systems for pumping ions
Q11: Why has C. elegans proven to be
Q27: Whether during mitosis or meiosis, sister chromatids
Q35: This solution has<br>A)used up all the reactants,
Q43: A reaction that absorbs free energy from
Q43: When Stanley Miller applied heat and electrical
Q67: Which of the following in the figure
Q69: You are working on a team that
Q79: MPF reaches its threshold concentration at the