Use the following information to answer the questions below.
A plantlike organism on the planet Pandora can have three recessive genetic traits: bluish leaves, due to an allele (a) of gene A; a feathered stem, due to an allele (b) of gene B; and hollow roots due to an allele (c) of gene C. The three genes are linked and recombine as follows:
A geneticist did a testcross with an organism that had been found to be heterozygous for the three recessive traits and she was able to identify progeny of the following phenotypic distribution (+ = wild type) :
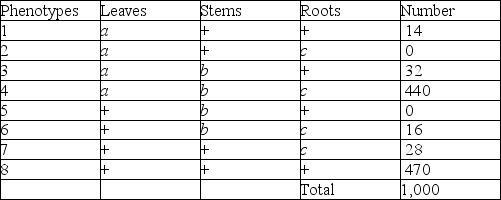
-What is the greatest benefit of having used a testcross for this experiment?
Definitions:
Adaptive Radiation
An evolutionary process in which organisms diversify rapidly into a multitude of new forms, particularly when a change in the environment makes new resources available or opens new niches.
Temporal Isolation
A mechanism of reproductive isolation where two species mate or flower at different times, preventing crossbreeding.
Reproductive Isolation
A set of mechanisms that prevent different species from interbreeding.
Ecological Isolation
A form of reproductive isolation where different species live in the same area but occupy different habitats, preventing them from mating and producing offspring.
Q4: Which pair would probably have agreed with
Q5: In an experiment, DNA is allowed to
Q29: A triploid cell contains three sets of
Q30: A space probe returns with a culture
Q33: Which component of the complex described enters
Q36: Bioinformatics can be used to scan sequences
Q53: Accuracy in the translation of mRNA into
Q61: In metabolic processes of cell respiration and
Q61: Which of the following can be determined
Q70: A dwarf, red snapdragon is crossed with