The next questions refer to the following table, which compares the % sequence homology of four different parts (two introns and two exons) of a gene that is found in five different eukaryotic species. Each part is numbered to indicate its distance from the promoter (e.g., Intron I is the one closest to the promoter) . The data reported for species A were obtained by comparing DNA from one member of species A to another member of species A.
% Sequence Homology
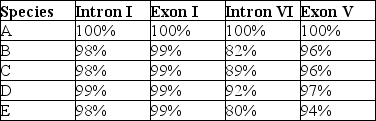
-Which of the following is the best explanation for the high degree of sequence homology observed in Exon I among these five species?
Definitions:
Internal Programs
Projects, initiatives, or plans developed within an organization to achieve specific goals, improve operations, or address internal needs.
Expectancy
The belief that one's effort will lead to attainment of desired performance goals.
Particular Level
A specific degree or stage in a process or hierarchy; often used to denote a focused or detailed layer within a broader context.
Second-level Outcome
Refers to indirect or subsequent effects that result from primary actions or interventions in a process or system.
Q12: Which of the following is an important
Q19: What is true of the flightless cormorants
Q27: Which eukaryotic kingdom is polyphyletic, and therefore
Q43: Which term accurately describes the behaviour of
Q48: According to a 1999 study, the vegetarian
Q53: Which population is most likely to be
Q69: As genetic technology makes testing for a
Q73: How were conditions on the early Earth
Q81: Sparrows with average-sized wings survive severe storms
Q94: A gymnosperm seed consists of a<br>A)sporophyte embryo