11.4 Consequences of Changes in Aggregate Demand
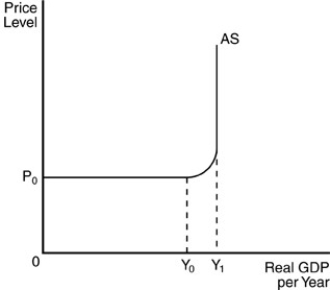
-Refer to the above figure. An increase in aggregate demand beyond real Gross Domestic Product (GDP) level Y₁ would result in
Definitions:
Equivalent Units
Equivalent units are a concept in cost accounting used to allocate costs to partially completed goods, treating them as if they were a certain number of fully completed units.
Job Order
A custom or production order that specifies the details for manufacturing a certain product or products for a customer.
Process Cost
The cost associated with a production process, allocated to products based on the process they go through rather than being directly traced to the product itself.
Conversion Costs
Conversion costs are the costs incurred to convert raw materials into finished products, including direct labor and manufacturing overhead.
Q16: Along a linear consumption function,<br>A)the average propensity
Q132: What could cause a decrease in the
Q139: An increase in the U.S. price level
Q147: Why is persistent unemployment a possibility in
Q221: In the above table, the marginal propensity
Q264: Some economists believe that a positive aggregate
Q268: Suppose total planned expenditures equal $20 trillion
Q278: When total planned real expenditures change due
Q287: The difference between savings and saving<br>A)is nonexistent.<br>B)is
Q414: In the above table, the average propensity