RESEARCH STUDY 11.2
(The first paragraph is repeated from earlier. The second paragraph is specific to the new set of questions. The first paragraph is necessary to set up the original study.)
Dr. Elder was interested in the way people recognize objects as members of categories. For example, what makes us recognize a dog as being a dog and not a cat? More specifically, he was curious as to whether people think about categories in a more complex way if they contemplate an "opposite" category first. For example, does a person think more differently about the category of "southern" if they are also thinking about the category of "northern"? He is also curious as to whether people categorize differently if they are exposed to category members compared with generating category members. Dr. Elder has four groups of participants (with 30 people in each group). In Group A, participants were told to cut out pictures of dogs and cats from magazines. In Group B, participants were told to cut out pictures of just dogs from magazines. In Group C, participants were told to draw pictures of cats and dogs. In Group D, participants were told to draw pictures of just dogs. After doing this for 30 minutes, participants in all groups were asked to list the attributes that define the "dog" category. Having a higher number of attributes listed was considered to be an indication of thinking about the category in a more complex way.
Dr. Elder also is curious as to whether categorization happens similarly for children as it does for adults. As such, he recruits a group of 10-year-olds and a group of 20-year-olds to participate in the study. The results are below.
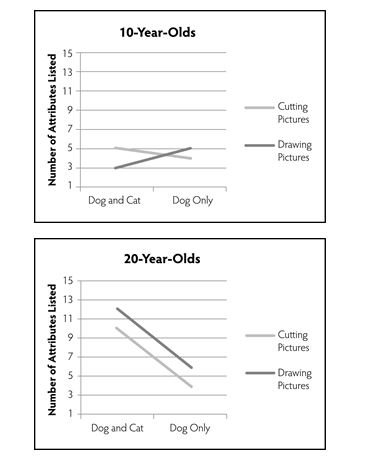
-Refer to Research Study 11.3 above to answer the following question.
Using factorial notation,describe Dr.Lopez's study.Given this information,how many main effects and interactions will Dr.Lopez need to examine?
Definitions:
Type II Error
The error made in statistical testing when a false null hypothesis is not rejected.
Null Hypothesis
A default hypothesis that there is no significant difference or relationship between specified populations or phenomena, used as a starting point for statistical testing.
Incorrect Decision
A decision based on data analysis or hypothesis testing that incorrectly accepts the null hypothesis or wrongly rejects it, leading to a Type I or Type II error.
Type II Error
The error that occurs when a statistical test fails to reject a false null hypothesis; also known as a "false negative."
Q1: Refer to Research Study 6.4 above to
Q13: The Spanish territories located closest to centers
Q27: Edward believes that there are a lot
Q30: The belief that the participants in a
Q32: The World Bank ranks countries within four
Q32: Refer to Research Study 3.4 above to
Q40: Name three disadvantages of within-groups designs.
Q44: Which of the following studies is most
Q83: Iquitos is Bolivia's "Atlantic port."
Q85: Argentina is the second-largest country in South