Insert non-labeled graph from page 150- replica created and inserted below 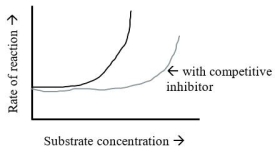
The graph shows the normal reaction rate of an enzyme and the reaction rate when a competitive inhibitor is present.Which description below explains the appearance of the graph?
Definitions:
Transient Ischemic Attack
A brief episode of neurological dysfunction caused by a temporary decrease in blood supply to part of the brain, often a warning sign for future strokes.
Myocardial Infarction
A medical condition commonly known as a heart attack, resulting from the interruption of blood flow to the heart.
Atrial Fibrillation
A quivering or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia) that can lead to blood clots, stroke, heart failure, and other heart-related complications.
Transient Ischemic Attack
Often called a mini-stroke, it's a brief episode of neurological dysfunction caused by loss of blood flow to the brain, spinal cord, or retina, without lasting damage.
Q4: In Table 7.1,which compound was bactericidal?<br>A)A<br>B)B<br>C)C<br>D)D<br>E)The answer
Q18: The use of an antibiotic-resistance gene on
Q20: How many pieces will EcoRI produce from
Q21: Which of the following is NOT a
Q35: Explain how the presence of algae can
Q38: In Figure 8.2,if base 4 is adenine,what
Q38: You have a small gene that you
Q41: A kitchen countertop has a spill of
Q42: Which of the following is incorrect?<br>A)Ethics is
Q49: Fungal infections are studied by<br>A)virologists.<br>B)bacteriologists.<br>C)parasitologists.<br>D)mycologists.<br>E)herpetologists.