in the following model of an atom, draw a transition from the first excited state to the third excited state. Then draw a transition from the third excited state to the second excited state. Then draw a transition from the second excited state to the first excited sate. To draw these, draw the electron's motion as a line with an arrow to indicate direction and draw the photon as a wave with an arrow to indicated direction. Label the electron and photon. Label whether this is an absorption, emission, or continuous spectrum. 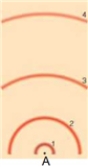
Definitions:
Standard Hours
The set number of hours that is expected to be used to complete a certain task or job in a manufacturing or project setting.
Actual Hours
The real number of hours worked or spent on a specific task or project, as opposed to planned or estimated hours.
Direct Labour Rate Variance
The difference between the actual wages paid to workers and the standard cost of those wages for the actual hours worked.
Labour Efficiency Variance
A metric used to measure the difference between the actual hours worked and the standard hours expected to complete a task.
Q59: In which way does a photon of
Q89: The carbon-nitrogen-oxygen cycle<br>A)operates at a slightly lower
Q91: Groombridge 34 is an M1 V star.
Q96: The _ of an object is a
Q98: The Orion region contains young main-sequence stars
Q100: A portion or all of the same
Q102: The above picture shows the Sun's change
Q136: Doppler-shift observations of a spectroscopic binary star
Q159: Why don't we see hydrogen Balmer lines
Q190: Below is a radial velocity curve for