Figure 10-9
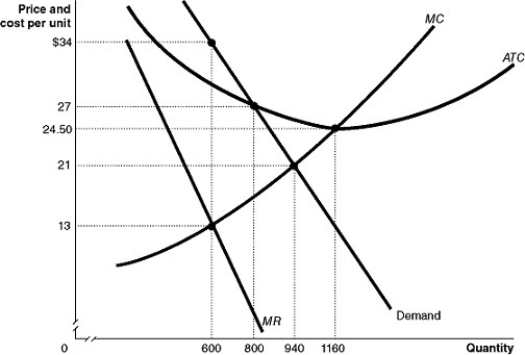 Figure 10-9 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
Figure 10-9 shows the demand and cost curves for a monopolist.
-Refer to Figure 10-9.What is the difference between the monopoly output and the perfectly competitive output?
Definitions:
Atmospheric Nitrogen
The form of nitrogen gas (N2) that makes up about 78% of the Earth's atmosphere, largely inert and not directly usable by most organisms.
Fungal Bodies
The physical structure of a fungus, including both the visible fruiting body and oftentimes an extensive network of hyphae known as the mycelium.
Vegetative Reproduction
A form of asexual reproduction in plants where new individuals are formed from the vegetative parts of the parent plant, such as roots, stems, or leaves.
Cellular Respiration
The metabolic process by which cells produce energy in the form of ATP from glucose, typically involving the consumption of oxygen and production of carbon dioxide.
Q25: A perfectly competitive firm will maximize its
Q61: Refer to Figure 10-18 to answer the
Q70: Refer to Figure 10-3.What happens to the
Q93: The Herfindahl-Hirschman Index is one factor used
Q108: Refer to Figure 10-2.The firm's profit-maximizing price
Q147: Provide two examples of a government barrier
Q170: Which one of the following about a
Q226: Assuming that the total market size remains
Q268: Refer to Table 9-4.If the market price
Q323: An oligopoly between two firms is called<br>A)