The figure shows a simple RC circuit consisting of a 10.0-µF capacitor in series with a resistor.Initially,the switch is open as suggested in the figure.The capacitor has been charged so that the potential difference between its plates is 100.0 V.At t = 0 s,the switch is closed.The capacitor discharges exponentially so that 2.0 s after the switch is closed,the potential difference between the capacitor plates is 37 V.In other words,in 2.0 s the potential difference between the capacitor plates is reduced to 37 % of its original value.
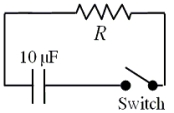
-Calculate the electric potential energy stored in the capacitor before the switch is closed.
Definitions:
Inflamed
A response of body tissues to injury or to the disruption of tissues, often characterized by redness, heat, swelling, pain, and sometimes loss of function.
Digestive System
A group of organs working together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body.
Digestive System
A collection of organs that work together to convert food into energy and basic nutrients to feed the entire body.
Hiatal Hernia
A condition in which part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, often causing discomfort and digestive problems.
Q6: The current through a certain heater wire
Q9: The largest potential difference is across which
Q13: While at the park,Tasha saw a small
Q21: What is the speed of an electron
Q34: Notren,Inc. ,a U.S.company,and SWT,a Singapore company,entered into
Q42: Which one of the following quantities is
Q43: Public hearings are required in formal administrative
Q43: Misleading commercial speech may be outlawed altogether
Q73: In a slide projector,the slide is illuminated;and
Q79: Which of the following samples exhibits the