In the Compton scattering experiment shown in the figure,a monochromatic beam of X-rays strikes a target containing free electrons.Scattered X-rays are detected with a wavelength of 2.50 × 10-¹² m at an angle of 45° away from the original beam direction.What is the wavelength of the incident monochromatic X-rays? Note: The mass of an electron is 9.11 × 10-³¹ kg. 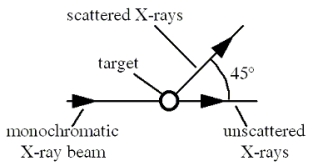
Definitions:
Pleadings
Documents filed with a court by parties to a legal action that detail their respective claims, defenses, and other material information relevant to the case.
English Courts
The judicial system in England and Wales, responsible for interpreting and applying English law in civil and criminal matters.
Equity
Refers to fairness or justice in the way people are treated or in the distribution of resources; in a financial context, it represents ownership interest in an asset or company.
Decree
A formal and authoritative order, often used in a legal context, such as a court decision or judgement.
Q1: Which one of the following statements concerning
Q4: The primary purpose of RICO was<br>A)to be
Q9: Ginger owns a business that is comprehensively
Q13: A 0.60-T magnetic field is directed perpendicular
Q18: Robert offers to buy a car from
Q44: Mavrex,Inc.received an application from Larry,and since his
Q45: What is the exclusionary rule and what
Q47: A transformer changes 120 V across the
Q50: Which one of the pipes emits sound
Q58: An ideal gas absorbs 750 J of