The figure below shows the demand (D) and supply (S) curves of a good produced domestically in an economy as well as traded in the international market. Figure 21.1 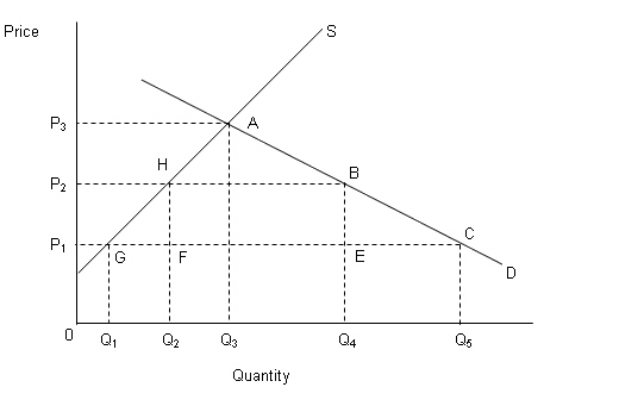 In the figure,
In the figure,
P1: Price of the good in the international market.
P2: Price of the good in the domestic market after the imposition of tariff by the government.
P3: No-trade price of the good in the domestic market.
-Refer to Figure 21.1.If the government imposes a tariff such that the price of the good in the domestic market is P2 when the international price is P1:
Definitions:
Long-Run Average Cost Curve
A graphical representation showing the lowest possible cost per unit that can be achieved for any given level of production when all factors of production are variable.
Average Total Cost
The aggregate expense of manufacturing (sum of constant and variable expenses) spread over the total units produced.
Marginal Cost
The upsurge in full costs resulting from the fabrication of an additional unit of a product or service.
Marginal-Cost Curve
A graphical representation showing how the cost to produce one additional unit of a good or service changes as production volume changes.
Q11: Federal judges can influence foreign policy by<br>A)issuing
Q14: If international trade is restricted by the
Q23: As three-quarters of the world's population resides
Q34: The people of Andres,a small fishing village
Q42: The supply curve of land in the
Q54: In Figure 17.1,the curve A indicates:<br>A)demand
Q57: Government restrictions prevent the market from allocating
Q60: The theory that lowering taxes will stimulate
Q74: Explain why Marbury v.Madison (1803) was a
Q84: Which of the following has resulted from