The figures given below represent the revenue curves of a monopolist. Figure 10.2 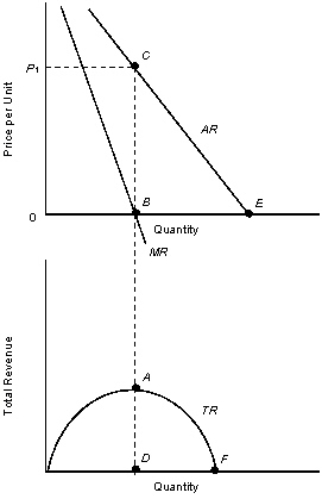
TR: Total revenue curve
AR: Average revenue curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
-Refer to Figure 10.2.In order to maximize profits,what quantity should the monopolist produce?
Definitions:
Tax
A required financial fee or another kind of duty enforced on a taxpayer by government authorities, designed to raise funds for government outlays and a range of public expenses.
Price-Elastic Supply
A situation where the quantity supplied of a good changes significantly as a result of changes in its price.
Excise Tax
A tax imposed on specific goods, services, or transactions, often included in the price of products like tobacco, alcohol, and fuel, to generate revenue or discourage consumption.
Price Elasticity
A measure of the responsiveness of the quantity demanded or supplied of a good or service to a change in its price.
Q9: Why is each firm in a monopolistically
Q13: When more and more doses of fertilizers
Q20: Which of the following is an example
Q26: Marginal revenue of n<sup>th</sup> unit of output
Q27: An automobile manufacturer uses land,labor,capital,and entrepreneurial ability
Q41: The primary goal of any business firm
Q62: When a divergence between social costs and
Q94: A perfectly competitive firm cannot affect the
Q94: When economists describe the theory of consumer
Q99: The only types of firms that cannot