The figure given below shows the revenue and cost curves of a perfectly competitive firm. Figure 9.2 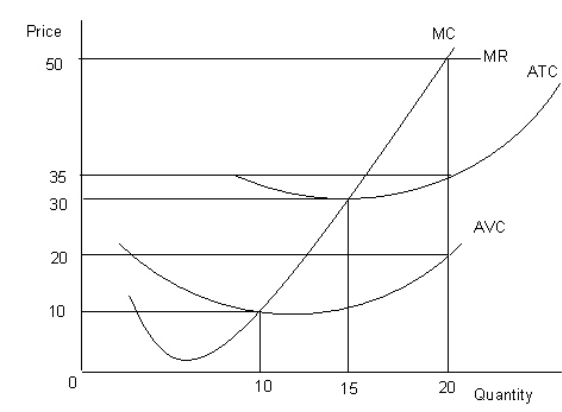
MC: Marginal cost curve
MR: Marginal revenue curve
ATC: Average-total-cost curve
AVC: Average-variable-cost curve
-Refer to Figure 9.2.If the marginal-revenue curve would have intersected the average-total-cost curve at its lowest point and the firm maximized profit,then total revenue would have been equal to:
Definitions:
Turner Syndrome
A chromosomal disorder affecting females, characterized by the partial or complete absence of one X chromosome, leading to various developmental issues.
Chromosomal Pattern
The specific arrangement and number of chromosomes within a cell, which can be analyzed to detect genetic disorders or anomalies.
XO
A genetic term referring to individuals with a single X chromosome and no second sex chromosome, typically associated with Turner syndrome.
Recessive Gene
A gene that is expressed in the phenotype only when it is on both chromosomes of a pair and not masked by a dominant gene.
Q31: The perfectly competitive market structure results in
Q37: Refer to Table 10.1.At what level of
Q47: In contrast to perfect competition,in a monopolistically
Q57: In Table 8.1,marginal revenue exceeds marginal cost:<br>A)until
Q83: A market failure occurs when the market
Q86: A downward-sloping demand curve is faced by
Q97: Under perfect competition,the average revenue curve of
Q100: In Figure 9.1,the firm's profit is equal
Q113: Refer to Figure 9.4.The presence of the
Q113: _ occurs when unobservable qualities are valued