The below indifference map shows the various combinations of hours of music and apples that yield different levels of utility. Figure 6.1 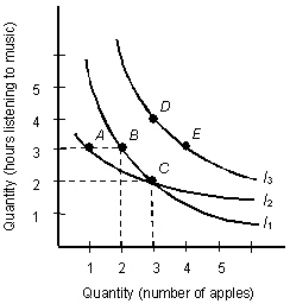
- Which of the following explains why indifference curve I2 should not cross indifference curve I1 as shown in Figure 6.1?
Definitions:
Assumptive Close
A sales technique where the seller assumes that the buyer has decided to make a purchase and moves forward with finalizing the sale, often by discussing next steps or payment options.
Purchase Decision
The process by which a consumer decides whether to buy a product or service, often influenced by factors such as need, desire, price, and brand loyalty.
Final Commitment
The ultimate agreement or decision made by a person or organization, often after a period of negotiation or consideration.
Limited Temporary Basis
A condition or period that is restricted in both scope and duration.
Q47: From Table 7.2,derive the value of total
Q63: In general,the two extreme cases of market
Q67: In the theory of utility,it is assumed
Q84: Due to the law of diminishing marginal
Q92: If a monopolist is producing at that
Q94: If you have a choice between studying
Q95: Given that resources can be allocated by
Q101: Refer to Figure 8.1.At price P<sub>1</sub>
Q104: Accounting profit is called normal profit when:<br>A)accounting
Q111: Under perfect competition,at the profit maximizing level