Using the graph, assume that the government imposes a $1 tariff on hammers. Answer the following questions given this information. 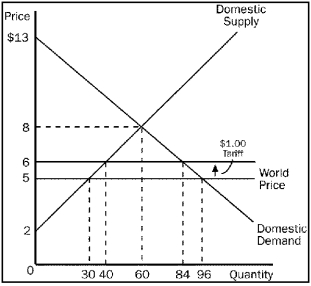
a. What is the domestic price and quantity demanded of hammers after the tariff is imposed?
b. What is the quantity of hammers imported before the tariff?
c. What is the quantity of hammers imported after the tariff?
d. What would be the amount of consumer surplus before the tariff?
e. What would be the amount of consumer surplus after the tariff?
f. What would be the amount of producer surplus before the tariff?
g. What would be the amount of producer surplus after the tariff?
h. What would be the amount of government revenue because of the tariff?
i. What would be the total amount of deadweight loss due to the tariff?
Definitions:
Managed Floating
An exchange rate system where a country's currency value is allowed to fluctuate in response to foreign-exchange market mechanisms, but the central bank can intervene to prevent extreme fluctuations.
Bretton Woods System
A monetary management system established post-World War II, which set up rules for commercial and financial relations among major industrial states.
Pegged Exchange Rates
A fixed exchange rate system where a country's currency value is fixed or pegged to another currency, a basket of currencies, or another measure of value.
Q37: Tim mows the yard for his neighbors.
Q60: In computing GDP, market prices are used
Q83: If nominal GDP is $12,000 and the
Q104: Which of the following is not an
Q126: Suppose Ecuador imposes a tariff on imported
Q142: Household spending on education is counted in
Q154: The price index was 150 in the
Q168: A tariff on a product makes<br>A)domestic sellers
Q261: Since it is counted as investment, why
Q282: Countries that restrict foreign trade are likely