Figure 21-6. On the left-hand graph, MS represents the supply of money and MD represents the demand for money; on the right-hand graph, AD represents aggregate demand. The usual quantities are measured along the axes of both graphs. 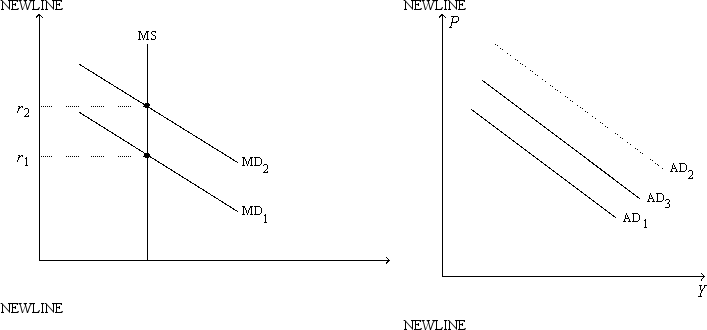
-Refer to Figure 21-6. Suppose the multiplier is 3 and the government increases its purchases by $25 billion. Also, suppose the AD curve would shift from AD1 to AD2 if there were no crowding out; the AD curve actually shifts from AD1 to AD3 with crowding out. Finally, assume the horizontal distance between the curves AD1 and AD3 is $30 billion. The extent of crowding out, for any particular level of the price level, is
Definitions:
Profit-Maximizing
A strategy or approach focused on increasing a firm’s profits to the highest possible level given its production costs and market demand.
Downward-Sloping
A characteristic of demand curves where price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions.
ATC Curve
A graphical representation of the average total cost of producing various quantities of output, showing how unit costs change with changes in output level.
AVC Curve
A graph that represents the average variable cost of producing each quantity of output, showing how these costs vary with changes in output levels.
Q44: In the equation, Unemployment rate = Natural
Q89: Refer to Scenario 21-2. The multiplier for
Q101: Refer to figure 22-7. If the economy
Q117: Suppose there were a large increase in
Q134: When government expenditures increase, the interest rate<br>A)increases,
Q184: Suppose the economy is in long-run equilibrium.
Q248: Refer to Figure 22-1. Suppose points F
Q264: Proponents of rational expectations argued that the
Q330: Other things the same, if the price
Q442: Suppose that the economy is at long-run