Figure 22-1. The left-hand graph shows a short-run aggregate-supply (SRAS) curve and two aggregate-demand (AD) curves. On the right-hand diagram, U represents the unemployment rate. 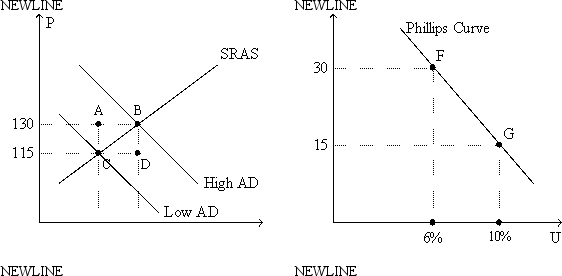
-Refer to Figure 22-1. Suppose points F and G on the right-hand graph represent two possible outcomes for an imaginary economy in the year 2012, and those two points correspond to points B and C, respectively, on the left-hand graph. Then it is apparent that the price index equaled
Definitions:
Excess Capacity
A situation where a company can produce more goods than the market demands, often leading to inefficiencies.
Monopolistic Competition
A market structure featuring many firms selling products that are similar but not identical, allowing for competition based on quality, price, and marketing.
Chronic Excess Capacity
A persistent situation in which industries or firms have more production capacity available than is being used, often leading to economic inefficiencies and reduced profit margins.
Minimum-Cost Output
The quantity of output at which the average total cost is lowest—the bottom of the U-shaped average total cost curve.
Q15: If aggregate demand shifts right, then eventually
Q69: A central bank sets out to reduce
Q76: A given short-run Phillips curve shows that
Q148: A policy that raised the natural rate
Q149: Which of the following are taxed?<br>A)both corporate
Q256: There are three factors that help explain
Q267: According to liquidity preference theory, a decrease
Q273: Assume the multiplier is 5 and that
Q332: If the long-run Phillips curve shifts to
Q348: An increase in the natural rate of