When 50.0 mL of 0.400 mol L-1 Ca(NO3) 2 is added to 50.0 mL of 0.800 mol L-1 NaF, CaF2 precipitates, as shown in the net ionic equation below. The initial temperature of both solutions is 23.0 °C. Assuming that the reaction goes to completion, and that the resulting solution has a mass of 100.00 g and a specific heat of 4.18 J g-1°C-1, calculate the final temperature of the solution. Ca2+(aq) + 2F-(aq) → CaF2(s) 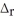 H = -11.5 kJ
H = -11.5 kJ
Definitions:
Increased Metabolic Demands
The body's need for more energy due to physical activity, growth, stress, or illness, requiring a higher intake of nutrients.
Decreased Drive
A reduction in the motivation or desire to engage in particular activities.
Fluid Volume Overload
A medical condition where there is an excessive accumulation of water and salt in the body, leading to swelling and other complications.
Increased Preload
A condition where the volume of blood in the heart's ventricles before contraction (end-diastolic volume) is increased, affecting the heart's function.
Q8: Which of the following signs on q
Q16: Which of the gases in the graph
Q21: Determine the molarity of a solution formed
Q43: Identify the most reactive alkali metal with
Q58: An element that has the valence electron
Q77: The vertical height of a wave is
Q142: A 2.38 g sample of phenol (C<sub>6</sub>H<sub>6</sub>O,
Q143: Place the following in order of increasing
Q159: Which of the following compounds is an
Q169: Determine the end (final)value of n in