Table 2.14 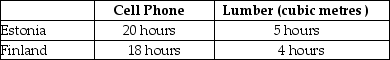
-Refer to Table 2.14.This table shows the number of labour hours required to produce a cell phone and a cubic metre of lumber in Estonia and Finland.
a. If each country has a total of 3,600 labour hours to devote to the production of the two goods, draw the production possibilities frontier for each country.Put "Cell Phone" on the horizontal axis and "Lumber" on the vertical axis.Be sure to identify the intercept values on your graphs.
b. Suppose each country allocates 55% of its labour hours to lumber production and 45% to the production of cell phones.Complete Table 2.15 below to show each country's output of the two products.
Table 2.15: Production and Consumption With No Trade 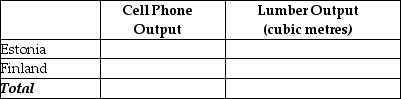 c. If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce, identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers.Label Estonia's consumption point "E" and Finland's consumption point "F."
c. If the two countries do not trade and consume whatever they produce, identify the current production and consumption point for each country on their respective production possibilities frontiers.Label Estonia's consumption point "E" and Finland's consumption point "F."
d. Suppose the two countries specialize and trade.Who should produce cell phones and who should produce lumber? Explain your answer.
e. Complete Table 2.16 below to show each country's output with specialization.
Table 2.16: Output With Specialization 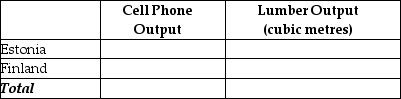 f. Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so, by how much?
f. Did specialization increase the combined output for the two countries without any increase in resources? If so, by how much?
g. Suppose Estonia and Finland agree to trade so that in exchange for 400 cubic metres of lumber, the exporter of lumber receives 90 cell phones.Complete Table 2.17 below to show each country's consumption bundle after trade.
Table 2.17: Consumption With Trade 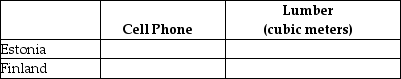 h.Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier.Label these points "X" for Estonia and "Y" for Finland.
h.Show the consumption points after trade on each country's production possibilities frontier.Label these points "X" for Estonia and "Y" for Finland.
i.Has trade made the two countries better off? Explain your answer.
Definitions:
Globalization
The method in which companies or various organizations gain global influence or begin to function at an international level.
Fieldwork
The collection of raw data and information through direct observation or engagement in a specific social, cultural, or physical environment, typically outside a laboratory or academic setting.
Ethnography
A detailed description of a particular culture primarily based on fieldwork.
Anthropological Approach
A method of study that focuses on understanding human cultures, behaviors, and societies, often through participant observation and fieldwork.
Q17: Refer to Figure 2.1.Point C is<br>A)technically efficient.<br>B)unattainable
Q27: Scientists always report their findings regardless of
Q52: Refer to Figure 2.2.The linear production possibilities
Q56: Refer to Table 4.6.Suppose that a simple
Q92: Positive analysis is concerned with "what ought
Q124: Changes in global weather patterns can lead
Q161: Suppose that when the price of hamburgers
Q172: The income earned by those who supply
Q221: Final consumption expenditures do not include household
Q271: What is the largest component of spending