Figure 3.8 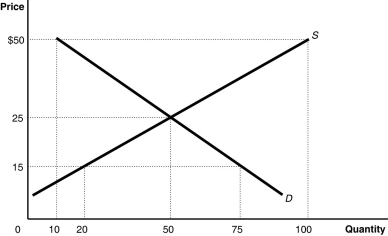 Alt text for Figure 3.8: In figure 3.8, a graph plotting intersecting supply and demand curves represents the market for canvas tote bags.
Alt text for Figure 3.8: In figure 3.8, a graph plotting intersecting supply and demand curves represents the market for canvas tote bags.
Long description for Figure 3.8: The x-axis is labelled, Quantity, with the values 0, 10, 20, 50, 75, and 100 marked.The y-axis is labelled, Price, with the values 0, 15, 25, and 50 dollars marked.Curve D is a straight line which slopes down from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.Curve S is a straight line which begins in the bottom left corner and slopes up to the top right corner.The equilibrium of the 2 curves is (50,25) .The point plotted on curve S to the left of equilibrium is (20,15) .The point plotted on curve D to the right of point of equilibrium is (75,15) .The point plotted to the right of equilibrium on curve S is (100,50) .The point plotted to the right of the equilibrium on curve D is (10,50) .
-Refer to Figure 3.8.The figure above represents the market for canvas tote bags.Assume that the price of tote bags is $15.At this price,
Definitions:
Accrued Expense
An accounting term for expenses that have been incurred but not yet paid, representing a company's obligation to make future payments.
Contra Account
An account in the general ledger that is used to reduce the value of a related account when the two are netted together.
Associated Account
An account linked or related to another in accounting, often used to track transactions connected to a specific business activity or party.
Plant Assets
Long-term tangible assets that are used in the production of goods or services and are not intended for sale.
Q14: Refer to Figure 2.3.Sergio Vignetto raises cattle
Q31: Suppose there is some unemployment in the
Q33: Which of the following would cause an
Q89: Refer to Figure 2.22.Which two arrows in
Q141: As incomes in Alberta fall people are
Q148: Which of the following describes actual trends
Q220: The labour force participation rates of men
Q256: Refer to Figure 2.13.Which country has a
Q276: In the circular flow model, households<br>A)sell goods
Q283: The basis for trade is comparative advantage,