Figure 8.3 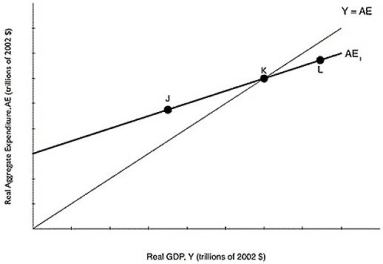 Alt text for Figure 8.3: In figure 8.3, a graph comparing real GDP and real aggregate expenditure.
Alt text for Figure 8.3: In figure 8.3, a graph comparing real GDP and real aggregate expenditure.
Long description for Figure 8.3: The x-axis is labelled, real GDP, Y (trillions of 2002 dollars) .The y-axis is labelled, real aggregate expenditure, AE (trillions of 2002 dollars) .Line Y = AE, originates at the vertex and slopes up to the top right corner.Line AE1, begins a little less than half way along the x-axis and slopes up to the end of the x-axis.Both these lines intersect at point K, approximately 3 quarters of the way along both lines.Point J is plotted a little less than half way along line AE1, to the left of point K.Point L is marked close to the right end of the line AE1, to the right of point K.
-Refer to Figure 8.3.If the economy is at point J, what will happen?
Definitions:
Forecast Method
Techniques used to predict future demand, sales, and other business metrics to guide decision-making.
Mean Absolute Deviation
A measure of variability that calculates the average absolute difference between each data point and the mean of a data set.
Tracking Signal
A technique used in forecasting to detect any bias in predicting future outcomes.
Holt's Model
Holt's Model is a forecasting technique that extends exponential smoothing to capture both level and trend in historical data, useful in predicting future values.
Q44: Consumer spending _ and investment spending _.<br>A)is
Q80: _ consumption is consumption that depends upon
Q89: In the long run, _ differences in
Q116: Hurricane Katrina destroyed oil and natural gas
Q164: Which of the following is not a
Q178: If a person withdraws $500 from his/her
Q186: A patent grants an inventor exclusive rights
Q199: Small differences in economic growth rates result
Q249: In a small Asian country, it is
Q257: If GDP per capita rises by 2%