Figure 9.3 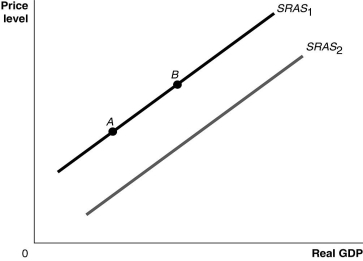 Alt text for Figure 9.3: In figure 9.3, a graph comparing real GDP and price level.
Alt text for Figure 9.3: In figure 9.3, a graph comparing real GDP and price level.
Long description for Figure 9.3: The x-axis is labelled, real GDP, with 0 at the vertex, and the y-axis is labelled, price level.2 lines are shown; SRAS1 and SRAS2.Line SRAS1 begins a little above the vertex and slopes up to the top right corner.Line SRAS2 follows the same slope as line SRAS1, but is plotted to the right.Points A and B are plotted on line SRAS1.Point A is near the left end of the line and point B is near the center of the line.
-Refer to Figure 9.3.Ceteris paribus, an increase in workers and firms adjusting to having previously overestimated the price level would be represented by a movement from
Definitions:
Legislation
Laws and statutes that are enacted by a legislative body through its legislative process.
Marginal Propensity
The portion of additional income that an individual spends on consuming goods and services, as opposed to saving.
Multiplier
An economic factor that quantifies the impact of a change in investment, government spending, or other economic variables on the overall economy, often leading to a multiple increase in income or output.
Liquidity Preference Theory
A theory suggesting that people prefer to hold their wealth in liquid form for ease of transactions and as a precaution against uncertainty, influencing interest rates.
Q51: The quantity theory of money implies that
Q100: A purchase and resale agreement implemented by
Q107: Ceteris paribus, how does an expansion in
Q127: Suppose the Bank of Canada purchases $10,000
Q142: When aggregate expenditure is more than GDP,
Q186: If the marginal propensity to save is
Q237: Globalization is defined as the process of
Q241: The major shortcoming of a barter economy
Q248: Which of the following will cause a
Q265: A person's wealth is the same as