Figure 13.2 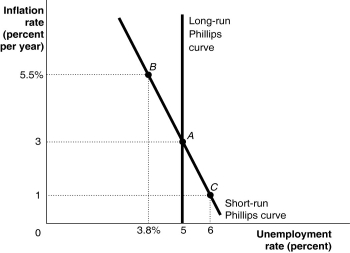 Alt text for Figure 13.2: In figure 13.2, a graph shows the short-run and long-run Phillips curves.
Alt text for Figure 13.2: In figure 13.2, a graph shows the short-run and long-run Phillips curves.
Long description for Figure 13.2: The x-axis is labelled, unemployment rate (percent) .The y-axis is labelled, inflation rate (percent per year) .3 points; A (5, 3) , B (3.8%, 5.5%) , C (6, 1) are plotted on the graph.The points are connected to their respective coordinates on the x and y-axes with dotted lines.A straight line labelled, short-run Philips Curve, begins at the top left corner and slopes down to the bottom center, and passes through points A, B, and C.A straight line labelled, long-run Philips Curve, is perpendicular to the x-axis, begins from the x-axis value 5,and intersects the Short-run Philips Curve at point A.
-Refer to Figure 13.2.Suppose the economy is at point C.If the Bank of Canada decreases the money supply so that inflation falls, the economy will ________ in the long run, holding all else constant.
Definitions:
Standard Deviation
A statistic that measures the dispersion or spread of a set of data points relative to its mean, used to quantify the amount of variation or dispersion in a set of data values.
P-chart
A type of control chart used for monitoring the proportion of defectives in a process over time in statistical quality control.
Control Limits
Statistical boundaries defined in control charts that indicate the acceptable range of variability in a process.
Process Capability Analysis
A statistical technique to determine if a process has the capability to produce products that meet specifications.
Q19: What is a mortgage? What were the
Q69: Write out the expression for the Taylor
Q92: Gold stored by Bank of Canada backs
Q104: Assume weak growth in aggregate demand keeps
Q105: The Bank of Canada uses the rate
Q113: The capital account records<br>A)transactions that affect net
Q118: Contractionary fiscal policy is used to decrease
Q122: If Canada is a "net borrower" from
Q203: If the government purchases multiplier equals 2,
Q256: Which of the following would be most