Figure 15.8 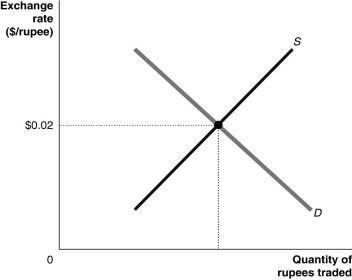 Alt text for Figure 15.8: In figure 15.8, a graph illustrates the quantity of rupees traded against the exchange rate.
Alt text for Figure 15.8: In figure 15.8, a graph illustrates the quantity of rupees traded against the exchange rate.
Long description for Figure 15.8: The x-axis is labelled, quantity of rupees traded.The y-axis is labelled exchange rate, Canadian dollar against the rupee, with value 0.02 marked.A straight line supply curve, S, slopes up from the bottom left corner to the top right corner.A straight line demand curve, D, slopes down from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.Curves S and D intersect at point with a y-axis value of 0.02, which is connected to the corresponding y-axis value with a dotted line.
-Refer to Figure 15.8.Which of the following is true?
Definitions:
Market Equilibrium
The condition in a market where the quantity of a product supplied is equal to the quantity demanded, often resulting in an equilibrium price.
Output Level
The quantity of goods or services produced by a company, industry, or economy within a specified period.
Private Value
Represents the worth or value of a good or service to an individual consumer, which may differ from its market price or cost to others.
Antibiotic-Resistant Diseases
Conditions caused by bacteria that have evolved to survive treatments with antibiotics previously effective against them.
Q3: Lisa manages customer service representatives in a
Q6: Total cost to produce is the sum
Q33: Between 1995 and 2013, foreign purchases of
Q44: Assuming Canada is the "domestic" country, if
Q49: A tenured professor lights a cigar,cradles a
Q51: A batch process is less flexible than
Q51: A tailor decides to use Taguchi's quality
Q125: What is the difference between a fixed
Q232: Currency traders expect the value of the
Q261: Which of the following would increase net