Figure 15.9 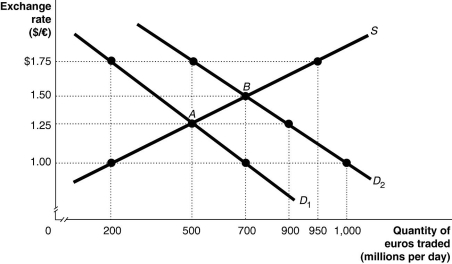 Alt text for Figure 15.9: In figure 15.9, a graph illustrates the quantity of euros traded against the exchange rate.
Alt text for Figure 15.9: In figure 15.9, a graph illustrates the quantity of euros traded against the exchange rate.
Long description for Figure 15.9: The x-axis is labelled, quantity of euros traded in millions per day.The y-axis is labelled, exchange rate, Canadian dollar against the euro.A straight line supply curve, S, slopes up from the bottom left corner to the top right corner.2 straight line demand curves, D1 and D2, slope down from the top left corner to the bottom right corner.Curve D2 is plotted to the right of curve D1.The difference between the curves is indicated by a right pointing arrow.Curve S intersects curves D1 and D2 at points A (500, 1.25) and B (700, 1.50) .Point (200, 1.00) is plotted near the bottom of curve S.Point (950, 1.75) is plotted near the top of curve S.Point (500, 1.75) is plotted near the top of curve D2.Points (900, 1.25) and point (1,000, 1.00) are plotted near the bottom of curve D2.Point (200,1.75) is plotted near the top of curve D1.Point (700, 1.00) is plotted near the bottom of curve D1.All points are connected to their corresponding values on the x and y-axes with dotted lines.
-Refer to Figure 15.9.The equilibrium exchange rate is at A, $1.25/euro.Suppose the European Central Bank pegs its currency at $1.00/euro.Speculators expect that the value of the euro will rise, and this shifts the demand curve for euros to D2.After the shift,
Definitions:
Trade Name
The name under which a business operates and is known to the public, distinct from the company's legal name.
Franchise
A business arrangement between an owner of a trade name or trademark and a person who sells goods or services under the trade name or trademark.
Trademark
A symbol, word, or phrase legally registered or established by use as representing a company or product.
Chain-style Business
A business model where multiple outlets are owned, franchised, or managed under a single brand or corporation.
Q5: The fill size for a small bag
Q6: What are the seven core ideas of
Q12: Volume flexibility is the term used to
Q21: Forecasting counts suppliers and customers among its
Q47: The Devon Tower graces the Oklahoma City
Q58: There is no need for an organizational
Q59: China began pegging its currency, the yuan,
Q65: Efforts to improve cooperation among firms in
Q110: A Big Mac costs $4.07 in Canada
Q147: If the U.S.government places tariffs on imports