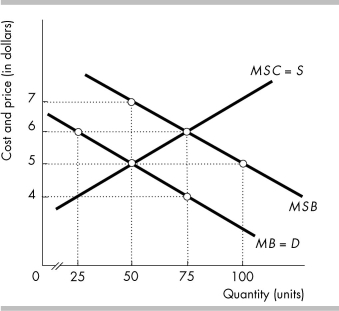
-In the above figure, if no government intervention occurs, at the unregulated competitive market equilibrium, there is an
Definitions:
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service supplied matches the quantity demanded, causing the market to be in a state of balance.
Equilibrium Price
The price at which the quantity of a good or service demanded equals the quantity supplied, leading to a stable market condition without excess supply or demand.
Supply and Demand
Fundamental economic model describing how the price and quantity of a good are determined in a market, based on the relationship between product availability and consumers' desire for it.
Determinant of Demand
A factor that affects the willingness and ability of consumers to buy a product, which can include price, income, tastes, and expectations.
Q36: Explain why a monopsony's marginal cost of
Q63: If a union is able to decrease
Q70: In a single payer model of healthcare,
Q80: Why does the labor supply curve eventually
Q177: The demand curve for labor is negatively
Q180: Use the idea of external costs to
Q200: The economy's marginal social benefit curve for
Q211: As the wage rate rises, the income
Q279: The value of marginal product (VMP) of
Q350: A labor market monopsony<br>A) has a marginal