A common application of Monte Carlo simulation is to provide numerical approximations. One such application is to approximate the area under a curve, or Monte Carlo integration. The following figure represents such a curve, defined over the range of X = 0 to X = 13. Call the area under this curve a.Monte Carlo integration begins by overlaying on the curve of interest a region (call this region, B) whose area is easy to calculate (i.e., a box). Monte Carlo integration then involves the random generation of points in B and a determination of the percentage of these points that fall in A (i.e., fall below the curve). This percentage represents that portion of the area of B that is the area of a.Use Monte Carlo integration techniques to approximate the area under the curve. Use exact techniques to calculate the true area under the curve. How accurate is your approximation? 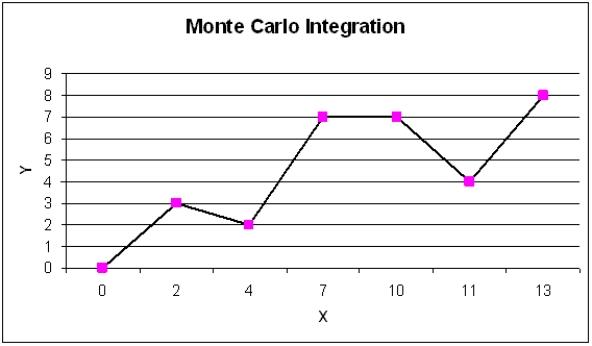
Definitions:
Cortex
The outer layer of the cerebrum of the mammalian brain, involved in higher brain functions such as thought and action.
Thalamus
A brain structure that processes and relays sensory information to the appropriate areas of the brain.
Neurons
Specialized cells that convey nerve signals, serving as the fundamental components of the nervous system.
Nerves
Bundles of axons coated in myelin that travel together through the body.
Q3: A corporation subject to AMT has AMT
Q10: How many local maximum solutions are there
Q20: Given the following goal constraints<br>5 X<sub>1</sub> +
Q37: A company needs to supply customers in
Q41: Calculate the annual inventory costs for the
Q51: Refer to Exhibit 15.3. The following spreadsheet
Q52: Refer to Exhibit 10.2. Based on the
Q72: Refer to Exhibit 9.1. Interpret the meaning
Q73: When using the Regression tool in Excel
Q120: If a shareholder receives cash from a