Exhibit 13.5
The following questions refer to the information and output below.
A computer printer in a large administrative office has a printer buffer (memory to store printing jobs) capacity of 3 jobs. If the buffer is full when a user wants to print a file the user is told that the job cannot be printed and to try again later. There are so many users in this office that we can assume that there is an infinite calling population. Jobs arrive at the printer at a Poisson rate of 55 jobs per hour and take an average of 1 minute to print. Printing times are exponentially distributed. The following queuing analysis spreadsheet was developed from this information. 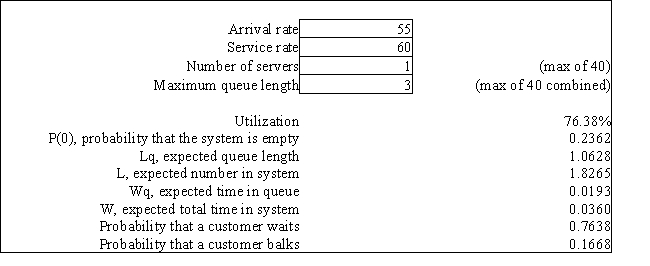
-Refer to Exhibit 13.5. What is the Kendall notation for this system?
Definitions:
Adenine
A nitrogenous base found in DNA and RNA, which pairs with thymine in DNA and uracil in RNA.
Thymine
One of the four nucleobases in the DNA molecule represented by the letter T, pairing with adenine (A).
Guanine
One of the four main nucleobases found in DNA and RNA, which pairs with cytosine in double-stranded DNA.
DNA Codon
A sequence of three nucleotides in DNA that specifies the inclusion of a particular amino acid in a protein or indicates a start or stop signal in protein synthesis.
Q25: Refer to Exhibit 11.3. What is
Q34: Although modeling provides valuable insight to decision
Q36: A convenience store chain is considering opening
Q43: A company wants to use PERT to
Q46: For AMT purposes,a taxpayer must use which
Q51: Refer to Exhibit 13.2. Based on this
Q65: A convenience store chain is considering opening
Q67: Refer to Exhibit 14.12. What is the
Q71: The terms <span class="ql-formula" data-value="\beta"><span
Q91: Which of the following statements are true