Use the data given below to construct a Born-Haber cycle to determine the second ionization energy of Ca. DH°(kJ)
Ca(s) → Ca(g) 193
Ca(g) → Ca⁺(g) + e⁻ 590.
2 O(g) → O2(g) -498
O(g) + e⁻ → O⁻(g) -141
O⁻(g) + e⁻ → O2⁻(g) 878
Ca(s) + 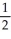 O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
O2(g) → CaO(s) -635
Ca2⁺(g) + O2⁻(g) → CaO(s) -3414
Definitions:
Sample Size
The count of data points or repeated measurements contained within a statistical sample.
Population Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or spread of all individual values from the mean of a population.
Sample Size
The number of observations or experimental units selected from a population for the purposes of statistical analysis.
Population Standard Deviation
A measure of the dispersion or variation of a set of values in a population, quantifying how much the values differ from the population mean.
Q1: If two electrons in the same atom
Q15: Magnesium burns in air with a dazzling
Q19: How many grams of AgNO<sub>3</sub> are needed
Q33: Identify the element that has a ground
Q47: The number 6.022 × 10<sup>23</sup> is called
Q62: How many argon atoms are contained in
Q74: Place the following in order of increasing
Q88: Give an example of a p orbital.
Q101: For hydrogen,what is the wavelength of the
Q139: Describe the difference between ionic and molecular