Table 16-1
The table below shows the total demand for viewing a rare penguin species at a local reserve. Ecotour companies have to build discreet viewing hides for tourists to view the penguins. Each ecotour company has to pay a fixed fee of $10 000 for the right to build on the reserve. Assume that hides can be supplied to tourists at zero marginal cost. Tickets are sold to tourists to use the viewing hides.
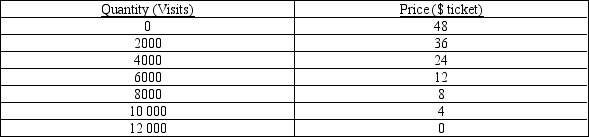 Any firm can change tickets by steps of 1000 only. Prices for missing quantities are the exact midpoint between two adjacent prices.
Any firm can change tickets by steps of 1000 only. Prices for missing quantities are the exact midpoint between two adjacent prices.
-Refer to Table 16-1. Assume that there are two profit-maximising ecotourist companies operating in this market. Further assume that they are not able to collude on price and quantity of the tickets they sell. How many tickets will be by each firms when this market reaches a Nash equilibrium?
Definitions:
Effective-interest Method
An accounting practice for amortizing the discount or premium on bonds or loans in a way that reflects a constant interest rate over the period.
Book Value
The net value of a company's assets minus its liabilities and intangible assets, often used to assess the company's worth.
Bond Liability
A financial obligation representing money owed by an issuer to the holder of the bond, to be repaid at a future date, along with periodic interest payments.
Straight-line Method
A depreciation method that allocates an equal amount of the asset's cost to each year of its useful life.
Q1: Graphically depict the deadweight loss caused by
Q13: The administrative burden of regulating price in
Q29: If a profit-maximising firm in a competitive
Q39: According to the information provided, advertising of
Q45: Why does a typical monopolistically competitive firm
Q60: If workers respond to an increase in
Q70: The degree of market failure caused by
Q74: The intent of competition laws is to
Q134: In a monopolistically competitive market structure, each
Q151: According to the information provided, even though